Ch.2 Questions: (Time: 20 minutes)
What is the first thing we should set up in Autodesk Inventor when creating a new model?
Describe the general parametric modeling procedure.
Describe the general guidelines in creating Rough Sketches.
What is the main difference between a rough sketch and a profile?
List two of the geometric constraint symbols used by Autodesk Inventor.
What was the first feature we created in this lesson?
How many solid features were created in the tutorial?
How do we control the size of a feature in parametric modeling?
Describe the steps required to define the orientation of the sketching plane?
List and describe three differences between parametric modeling and traditional 2D Computer Aided Drafting techniques.
Ch.3 Questions: (Time: 20 minutes)
List and describe three basic Boolean operations commonly used in computer geometric modeling software?
What is a primitive solid?
What does CSG stand for?
Which Boolean operation keeps only the volume common to the two solid objects?
What is the main difference between a CUT feature and a HOLE feature in Autodesk Inventor?
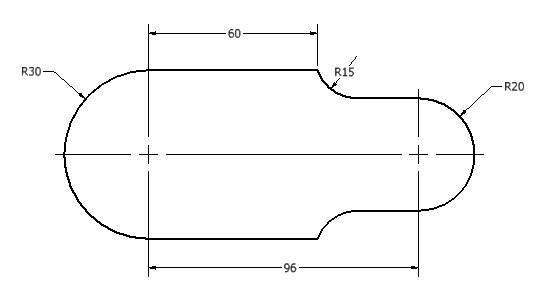
Create the following 2D Sketch and measure the associated area and perimeter.
Using the CSG concepts, create Binary Tree sketches showing the steps you plan to use to create the two models shown on the next page:
Ch.4 Questions: (Time: 30 minutes)
What are stored in the Autodesk Inventor History Tree?
When extruding, what is the difference between Distance and Through All?
Describe the history-based part modification approach.
What determines how a model reacts when other features in the model change?
Describe the steps to rename existing features.
Describe two methods available in Autodesk Inventor to modify the dimension values of parametric sketches.
Create History Tree sketches showing the steps you plan to use to create the two models shown on the next page:
Ch.5 Questions: (Time: 30 minutes)
What is the difference between dimensional constraints and geometric constraints?
How can we confirm that a sketch is fully constrained?
How do we distinguish between derived dimensions and regular dimensions on the screen?
Describe the procedure to Display/Edit user-defined equations.
List and describe three different geometric constraints available in Autodesk Inventor.
Does Autodesk Inventor allow us to build partially constrained or totally unconstrained solid models? What are the advantages and disadvantages of building these types of models?
How do we display and examine the existing constraints that are applied to the sketched entities?
Describe the advantages of using parametric equations.
Can we delete an applied constraint? How?
Describe the purpose and usage of the Auto Dimension command.
Ch. 6 Questions: (Time: 25 minutes)
What are the two types of wireframe geometry available in Autodesk Inventor?
Can we create a profile with extra 2D geometry entities?
How do we access the Autodesk Inventor’s Edit Sketch option?
How do we create a profile in Autodesk Inventor?
Can we build a profile that consists of self-intersecting curves?
Describe the procedure to create a copy of a sketched 2D wireframe geometry?
Can we create additional entities in a 2D sketch, without using them at all?
How do we align the sketch plane of a selected entity to the screen?
Describe the steps we used to switch existing profiles in the tutorial?
Describe the advantages of using the Offset command vs. creating a separate sketch.
Ch. 7 Questions: (Time: 25 minutes)
Why is it important to consider the parent/child relationships in between features?
Describe the procedure to suppress a feature.
What is the basic concept of the BORN technique?
What happen to a feature when it is suppressed?
How do you identify a suppressed feature in a model?
What is the main advantage of using the BORN technique?
Create sketches showing the steps you plan to use to create the models shown on the next page:
Ch. 8 Questions: (Time: 25 minutes)
What does Autodesk Inventor’s associative functionality allow us to do?
How do we move a view on the Drawing Sheet?
How do we display feature/model dimensions in the drawing mode?
What is the difference between a feature dimension and a reference dimension?
How do we reposition dimensions?
What is a base view?
Can we delete a drawing view? How?
Can we adjust the length of centerlines in the drafting mode of Inventor? How?
Describe the purpose and usage of the Leader Text command.
Describe the advantages of using the 3D annotations in isometric drawing views approach as a documentation tool that is available in Autodesk Inventor.
Ch. 9 Questions: (Time: 25 minutes)
What are the different types of work features available in Autodesk Inventor?
Why work features are important in parametric modeling?
Describe the purpose of auxiliary views in 2D drawings?
What are the required elements in order to generate an auxiliary view?
Can we use a different Title Block in the Drawing Mode? How?
Describe the different methods used to create centerlines in the chapter.
Can we change the View Scale of existing views? How?
What is the main difference between an auxiliary view and a projected view in Autodesk Inventor?
Describe the steps to change the display style of a drawing view.
Describe the difference between the centerlines created with the Centerline Bisector and the Center Mark commands.
Ch. 10 Questions: (Time: 25 minutes)
List the different symmetrical features created in the Pulley design.
What are the advantages of using a drawing template?
Describe the steps required in using the Mirror Feature command.
Why is it important to identify symmetrical features in designs?
When and why should we use the Pattern option?
What are the required elements in order to generate a sectional view?
How do we create a Linear Diameter dimension for a revolved feature?
What is the difference of construction geometry and normal geometry?
List and describe the different centerline options available in the Drawing Annotation panel.
What is the main difference between a sectional view and a projected view?
Ch. 11 Questions: (Time: 25 minutes)
Keeping the History Tree in mind, what is the difference between cut with a pattern and cut each one individually?
What is the difference between Sweep and Extrude?
What are the advantages and disadvantages of creating fillets using the 3D Fillets command and creating fillets in the 2D profiles?
Describe the steps used to create the Shell feature in the lesson.
How do we modify the Pattern parameters after the model is built?
Describe the elements required in creating a Swept feature.
Create sketches showing the steps you plan to use to create the model shown on the next page:
Ch. 12 Questions: (Time: 30 minutes)
List and describe two of the more commonly used sheet metal processes.
Is it possible to construct a solid model first, then convert it into a sheet metal model in Autodesk Inventor?
Which command do we issue to display the flat pattern of a 3D sheet metal design?
What is the k-factor used in sheet metal processes?
How is k-factor used to calculate the flattened length in sheet metal flat patterns?
List and describe two of the factors that can change the k-factor value.
List and describe two of the settings available in the Sheet Metal Defaultsin Autodesk Inventor.
List and describe the differences in between the Flange and Face commands.
Can the Retrieve Dimensions command be used on a flat patternview?
What does the Pivot 180 option allow us to do when creating a drawing view?
In the Autodesk Inventor sheet metal module, can the feature-duplicating commands, such as Mirror and Pattern, be used on sheet metal features?
In the Drawing View dialog box, which option allows us to display the flat pattern of the sheet metal design?
Is the flat pattern item always available in the sheet metal part Browser window?
Can we create a sheet metal feature that is at a 30 degree angle to the base face feature? Which command would you use if the new feature contains fairly complex 2D geometry?
Questions: (Time: 35 minutes)
What is the purpose of using assembly constraints?
List three of the commonly used assembly constraints.
Describe the difference between the Mate constraint and the Flush constraint.
In an assembly, can we place more than one copy of a part? How is it done?
How should we determine the assembly order of different parts in an assembly model?
How do we adjust the information listed in the parts list of an assembly drawing?
In Autodesk Inventor, describe the procedure to create a bill of materials (BOM)?
Create sketches showing the steps you plan to use to create the four parts required for the assembly shown on the next page:
Ch. 14 Questions: (Time: 30 minutes)
What is included in the Autodesk Content Center?
What is the usage of 3D grips?
How do you save the Inventor simulation as an AVI or MS WMV movie?
How do you access the Drive Constraint command?
List and describe two of the assembly constraints that can be used to drive the simulation with the Drive Constraint command.
How do we enter the Edit mode in an assembly model?
Can we access the 2D sketch of a feature of a part in an assembly?
How do we end the Edit mode and return to the assembly model in Autodesk Inventor?
List and describe two methods to edit the angle of an Angle constraint.
Describe the procedure to perform an Interference Analysis in an assembly.
What information is available through the Interference Analysis in Autodesk Inventor?
How do you control the speed of the simulation in Autodesk Inventor?
Ch. 15 Questions: (Time: 25 minutes)
Briefly describe the concept of 2D Design Reuse. Describe some of the advantages of 2D Design Reuse.
Can AutoCAD DWG files be opened and saved with Autodesk Inventor?
Can we edit the AutoCAD DWG entities that are in AutoCAD Model Space under Autodesk Inventor?
Can we edit the AutoCAD DWG entities that are in AutoCAD Layout under Autodesk Inventor?
List and describe three commands available in the Drawing Review Panel?
What does the >Contact Solverallow us to do?
Describe the steps involved in using the Inventor Contact Solver.
Can we perform a constrained move on fully constrained components?
Can Autodesk Inventor calculate the center of gravity of an assembly model? How do you activate this option?
Can assembly constraints be temporary disabled in an assembly model? How?
When and why would you use the Collision Detection option available in Autodesk Inventor?
Can Autodesk Inventor calculate the weight of an assembly model? How is this done?
Source: http://www.oit.edu/faculty/randy.shih/mech407/ChQuestions.doc
Web site to visit: http://www.oit.edu
Author of the text: indicated on the source document of the above text
Instructors Guide - Questions & Answers
by
Daniel T. Banach, Travis Jones & Alan J. Kalameja
Introduction Notes
To ensure students will get the most out of this class confirm that all the students are proficient in the basic use of Windows commands and operations. This book does not cover basic Windows operations. To give your students a better understanding of Autodesk Inventor's power and capabilities, present to the class the creation of a simple part and assembly. This will show the students the ease of use and power behind Autodesk Inventor.
When working through this book each student should work through all of the tutorials and exercises on their own, this will build proficiency. Each chapter builds on the previous chapter. As the students complete each tutorial and exercise they should feel free to experiment with other methods of completing the tutorial and exercise. The geometry in the first few chapters is simpler in nature to ensure the students understand the methodology of Autodesk Inventor. As the book progresses, the amount of help given in the tutorials and exercises will decrease.
Project Exercises
Near the back of each chapter is a self-paced step-by-step project exercises are found at the end of each chapter and provide an opportunity for you to work through real-world modeling, assembly and documentation tasks. The geometry used in the project exercises will flow from chapter to chapter utilizing the functionality you learned in that chapter. The project exercises are based upon a coating system gripper station design. The specifications for the design define a modular gripper station that can be cycled through several cleaning, coating spin and curing stations. All stations need to work within a particulate free laminar air flow environment.
Applying Your Skills Exercises
After the Project Exercise in chapter 2 – 10 there is an Applying Your Skills exercise(s) which is an exercise that allows the student to complete the exercise with limited amount of instruction. The exercise reinforces the topics covered in that chapter.
To review the design in more detail, open the IV11-CH1-PE-Overview.dwf file found in the following location: Your Drive:\IV11 Essentials Plus\Exercises\. The DWF file represents the finished assembly.
Chapter 1
CHECKING YOUR SKILLS
1 Explain the reasons for which a project file is used.
Projects are text files that contain search paths to find files that are needed for a given project. With these search paths, all the needed files can be located when an assembly, drawing, or presentation file is opened.
2 True___ False___ Only one project can be active at any time.
3 List the sequence of the locations searched when a file is opened in Autodesk Inventor.
4 True___ False___ Autodesk Inventor stores the part, assembly information, and related drawing views in the same file.
False, While creating parts, assemblies, presentation files, and drawing views, that data is stored in separate files with different file extensions.
5 True___ False___ Press and hold down the F4 key to dynamically rotate a part.
6 True___ False___ The Save Copy As command saves the active document with a new name and then makes it current.
False, the Save Copy As command saves the active document with a new name but it does NOT make the new file active.
7 List four ways to access the Help system.
8 Explain how to create a shortcut.
9 True___ False___ The Look At tool changes the viewpoint to an isometric view.
False, The Look At tool changes the viewpoint so you are looking parallel to a plane, or rotates the screen viewpoint to be horizontal to an edge.
10 True___ False___ You can only edit a part while it is in shaded display.
False, You can choose Shaded Display, Hidden Edge Display, or Wireframe Display mode as you see fit.
Chapter 2
CHECKING YOUR SKILLS
1 True___ False___ When sketching, constraints are not applied to the sketch by default.
False. While sketching, small constraint symbols appear that represent geometric constraint(s) that will be applied to the object. If you do not want a constraint to be applied, hold down the CTRL key when the point is selected.
2 True___ False___ When sketching and a point is inferred, a constraint is applied to represent that relationship.
False, When inferred points are selected, no constraints (geometric rules such as horizontal, vertical, collinear, etc.) are applied from them. Using inferred points helps create more accurate sketches.
3 True___ False___ A sketch does not need to be fully constrained.
True, Autodesk Inventor does not force you to fully constrain a sketch. It is recommended to fully constrain a sketch, however, as this will allow you to better predict how a part will react when dimensions values are changed.
4 True___ False___ When working on a mm part, you cannot use English units.
False, The default unit for any value can be overridden by entering in the desired unit.
5 True___ False___ After a sketch is constrained fully, you cannot change a dimension’s value.
False, To edit a dimension that has already been created, double-click on the value of the dimension and enter a new value in the Edit Dimension dialog box.
6 True___ False___ A driven dimension is another name for a parametric dimension.
False, A driven dimension is a reference dimension. It is not a parametric dimension it just reflects the size of the points to which it is dimensioned. A driven dimension will appear with parentheses around the dimensions value, like (30).
7 If you use the Auto Dimension tool on the first sketch in the part, the sketch will be constrained fully.
False, If you use the Auto Dimension tool on the first sketch in the part, two dimensions or constraints will be required to fully constrain the sketch. Constrain or dimension the sketch to the projected part orign or use the Fix constraint, or constrain or dimension to the projected origin planes, or axis to remove the two required dimensions.
8 True___ False___ You can only import 2D AutoCAD data into Autodesk Inventor.
False, many file types can be imported into Autodesk Inventor, including the following files types; AutoCAD (2D and 3D), AutoCAD Mechanical, Mechanical Desktop, SAT, STEP, PRO/E, DXF, and IGES.
9 Explain how to draw an arc while still in the Line command.
While using the line tool move the cursor over an endpoint and a small circle will appear at that endpoint. Click on the small circle, and with the left mouse button pressed down, move the cursor in the direction that you want the arc to go. Depending upon how you move the mouse, up to eight different arcs can be drawn.
10 Explain how to remove a geometric constraint from a sketch.
Click the Show Constraints tool from the Sketch Panel Bar. Select an object and a row of constraint icons
will appear, move the cursor over a constraint icon, the objects that are linked to that constraint will change color. Then, either click on it and then right-click, or right-click while the cursor is over the constraint and select Delete on the menu.
11 Explain how to change a vertical dimension to an aligned dimension while create create it.
The technique to change the constraint is called scrubbing. To place a different constraint while sketching, move the cursor so it touches (scrubs) the other object to which the constraint should be related. Move the cursor back to its original location and the constraint symbol changes to reflect the new constraint.
12 Explain how to create a dimension between two quadrants of two arcs.
Chapter 3
CHECKING YOUR SKILLS
1 What is a base feature?
The first sketch of a part that is used to create a 3D feature.
2 True___ False___ When creating a feature with the Extrude or Revolve tool, you can drag the sketch to define the distance or angle.
True
3 Which objects can be used as an axis of revolution?
A straight edge, centerline, or line can be used as an axis of revolution. The edge does not need to be part of the sketch.
4 Explain how to create a diametric dimension on a sketch.
Use the General Dimension tool and select either a centerline and the other point or line to be dimensioned, or click a point or edge and then the centerline. You can also right-click in the graphics window and select Linear Dimension with the General Dimension tool active.
5 Name two ways to edit an existing feature.
6 True___ False___ Once a sketch becomes a base feature, you cannot delete or add constraints, dimensions, or objects to the sketch.
7 Name three operation types used to create sketched features.
8 True___ False___ A cut operation cannot be performed before a base feature is created.
True, there must be an existing solid to remove (cut) material from.
9 True___ False___ Once a sketched feature exists, its termination cannot be changed.
False, you can edit a sketched feature and modify the termination that is used.
10 True___ False___ Geometry that is projected from one feature to a sketch that defines another feature will update automatically based on changes to the original projected geometry.
True
Chapter 4
CHECKING YOUR SKILLS
1 True___ False___ When creating a fillet feature that has more than one selection set, each selection set appears as an individual feature in the Browser.
False. When multiple selection sets exist, they are created as a single fillet feature.
2 In regards to creating a fillet feature, what is a smooth radius transition?
The fillet feature blends from the start to the end radius as a smooth transition, similar to a cubic spline. Otherwise the fillet blends from the start to the end radius as a straight line.
3 True___ False___ When creating a fillet feature with the All Fillets option, material is removed from all concave edges.
True
4 True___ False___ When creating a chamfer feature with the Distance and Angle option only one edge can be chamfered at a time.
False, multiple edges can be selected when using the Distance and Angle option of the Chamfer feature.
5 True___ False___ When creating a Hole feature, you do not need to have an active sketch.
True, although you can create a hole feature when a sketch is active, you can also use the Concentric, On Point, and Linear options to create a hole feature without having a sketch active.
6 For what purpose is a Point, Center Point used?
Hole Center’s are used to represent the center of the hole(s) that will be placed with the Hole tool when using the From Sketch option.
7 True___ False___ Thread features are represented graphically on the part and will be annotated correctly when drawing views are generated.
True – After the drawing view(s) have been created use the Hole / thread Note tool to annotate the thread in the drawing.
8 True___ False___ A part may contain only one shell feature.
False, you can create multiple shell features in a part.
9 When creating a face draft feature, what is the definition of pull direction?
The pull direction is used to specify how the mold will be pulled from the part. The angle of the face draft feature expands in this direction.
10 True___ False___ The only method to create a work axis is by clicking a cylindrical face.
False, some additional methods to create a work axis besides a cylindrical face are:
11 True___ False___ You need to derive every new sketch from a work plane feature.
False, you can use any planar face or work plane to create a new sketch.
12 Explain the steps to create an offset work plane.
13 True___ False___ You cannot create work planes from the default work planes.
False, you can reference the default work planes to create any type of work plane that needs a planar face as input for its definition.
14 True___ False___ When you are creating a rectangular pattern, the directions along which the features are duplicated must be horizontal or vertical.
False, you can reference any edge to be used as a direction for a rectangular pattern. The edge can be at an angle, horizontal, vertical, or a spline.
15 True___ False___ When you are creating a circular pattern, you can only use a work axis as the axis of rotation.
False, you can use any edge, axis or circular face.
Chapter 5
CHECKING YOUR SKILLS
1 True___ False___ A drawing can have an unlimited number of sheets.
TRUE. There is no limit to the number of drawing sheets you can have in a drawing.
2 True___ False___ A drawing’s sheet size is normally scaled to fit the size of the drawing views.
FALSE. It is the scale of the drawing views that are normally scaled to fit the drawing sheet size.
3 True___ False___ There can only be one base view per sheet.
FALSE. A number of base views can be created on a single drawing sheet. This is especially useful when arranging many parts on the same drawing sheet.
4 True___ False___ An isometric view can only be projected from a base view.
FALSE. Isometric views can be projected from any drawing view.
5 True___ False___ Auxiliary views typically show internal features of a part that have been cut.
FALSE. An auxiliary view is a view that is projected perpendicularly to a selected edge or a line. When showing internal features of a part that has been cut, a section view operation is performed.
6 True___ False___ Drawing dimensions can parametrically drive dimensional changes back to the part.
FALSE. Drawing reference dimensions cannot parametrically drive dimensional changes back to the part. Parametric model dimensions displayed in a drawing view can parametrically drive dimensional changes back to the part.
7 Explain how to shade an isometric drawing view.
Use the following steps to shade an isometric drawing view:
8 True___ False___ When creating a hole note using the Hole/Thread Notes tool, circles that are extruded to create a hole can be annotated.
FALSE. The Hole/Thread Notes tool will not add annotations to holes that were created as extrusions. This tool is most effective when annotating features such as holes, counterbores and countersinks created with the Hole tool.
9 True___ False___ Model dimensions cannot be used or imported into drawing views.
FALSE. The Retrieve Dimensions tool allows you to select valid model dimensions for display in a drawing view.
10 True___ False___ When selecting drawing view objects, clicking and dragging your cursor from the left to the right will create a crossing selection box.
FALSE. Clicking and dragging your cursor from left to right will create a window selection box. To create a crossing selection box, click and drag your cursor from right to left.
Chapter 6
CHECKING YOUR SKILLS
1 True___ False___ The only way an assembly can be created is by placing existing parts into it.
FALSE. You can also create a part inside of an assembly.
2 Explain top-down and bottom-up assembly techniques.
The Top-Down assembly technique is used where you create new components while in an assembly model.
The Bottom-Up assembly technique uses external files that are referenced into the assembly. The components that make up the assembly in this approach are created as individual files.
3 True___ False___ An occurrence is a copy of an existing component.
TRUE
4 True___ False___ Only one component can be grounded in an assembly.
FALSE. More than one component can be grounded in an assembly file.
5 True___ False___ Autodesk Inventor does not require components in an assembly to be fully constrained.
TRUE. However underconstraining a component would result in the assembly acting unstable.
6 True___ False___ A sketch must be fully constrained to adapt.
FALSE. You typically underconstrain a sketch allowing it to adapt when placed in an assembly file.
7 What is the purpose of creating a presentation file?
Creating a presentation file will allow you to demonstrate how parts in an assembly interact with each other. An exploded presentation can be created of an assembly to expose parts that would otherwise be hidden from view. Animations can be created that show how parts are assembled or disassembled.
8 True___ False___ A presentation file is associated to the assembly file on which it is based.
TRUE
9 True___ False___ When creating drawing views from an assembly, you can create views from multiple presentation views or design view representations.
TRUE
10 True___ False___ When creating automatic balloons, you can control the duplication of balloons based on various occurrences of the same part.
TRUE
Chapter 7
CHECKING YOUR SKILLS
1 True___ False___ You can dimension to geometry that uses the construction style.
True, Construction geometry can be constrained and dimensioned like normal geometry, but the construction geometry will not be seen in the part when the sketch is turned into a feature.
2 True___ False___ Splines cannot have geometric constraints applied between them and other geometry.
False, Constraints can be added to any visible handlebars, curvature arc, or flat of any point on a spline. The following constraints can be added: concentric, equal, collinear, horizontal, perpendicular, parallel, tangent, and vertical.
3 True___ False___ The points that are imported from an Excel spreadsheet using the Import Points tool are associative to the spreadsheet.
False,the imported points have no relationship back to the data in the spreadsheet
4 True___ False___ Modifications to a shared sketch will update all the features that use that shared sketch.
5 True___ False___ Slice Graphics will permanently slice away a portion of the model.
False, The Slice Graphics option will temporarily slice away the portion of the model that obscures the plane on which you want to sketch. To restore the sliced graphics, right-click and select Slice Graphics, select Slice Graphics from the View menu, or click the Sketch or Return button from the Command Bar to end the sketch.
6 True___ False___ The Project tool can project vertices, work features, curves, or silhouette edges of another part in an assembly to the active sketch.
7 True___ False___ When creating parameters in a spreadsheet, the data items must be in the following order: parameter name, value or equations, unit of measurement and, if needed, a comment.
True, however only the parameter name and value fields are required.
8 Explain how to suppress a patterned occurrence.
To suppress a patterned occurrence, move the cursor over an occurrence in the pattern and right-click. A menu will appear, click Suppress Element(s) and then select the occurrence (s) that will be suppressed.
9 What is the difference between a Model Parameter and a User Parameter?
10 What is a reference parameter?
This A reference parameter is created automatically when you create a driven dimension. Autodesk Inventor assigns a default name to each reference parameter as you create it. The default name format is a ‘‘d’’ followed by an integer incremented for each new parameter. You can rename reference parameters via the Parameters dialog box.
Chapter 8
CHECKING YOUR SKILLS
1 True___ False___ When creating a single rib or a web feature, you can only select a closed profile.
False, A rib or web feature is defined by an open, unconsumed profile that is then refined using the options in the Rib dialog box.
2 True___ False___ Both the Extrude and Revolve tool can use the minimum or maximum extrusion solution.
False, The Extrude tool is the only tool that utilizes the minimum or maximum extrusion solution.
3 True___ False___ You can only place embossed text on a planar face.
.
False, A closed shape or text can be embossed or engraved onto a planar or curved face.
4 True___ False___ A sweep feature requires three unconsumed sketches.
False, A sweep feature requires two unconsumed sketches—a profile, and a path that the profile will follow. A guide rail or surface can also be used to define the sweep.
5 True___ False___ You can create a 3D curve with a combination of both 2D and 3D curves.
6 Explain how to create a 3D path using geometry that intersects with a part.
7 True___ False___ The easiest way to create a helical feature is to create a 3D path and then sweep a profile along this path.
False, Use the Coil tool.
8 True___ False___ You can control the twisting of profiles in a loft by defining point sets.
True, A point set is used to define how segments blend from one section to the segments of the section
before and after it.
9 Explain how to save both halves of a part after splitting it.
To create a part with the other side removed, edit the split feature and redefine it to keep the other side, save the other half of the part to its own file using the Save As command.
10 True___ False___ You can copy features between parts using the Copy Feature tool on the Part Features Panel Bar or toolbar.
False,
11 Explain the difference between suppressing and deleting a feature.
12 True___ False___ After mirroring a feature, the mirrored feature is independent from the parent feature. If the parent feature changes, the mirrored feature will not reflect this change.
False, The mirrored feature(s) will be dependent on the parent feature—if the parent feature changes, the resulting mirror feature will also update to reflect the change.
13 Explain why you would want to override a part's mass and volume properties.
While designing, you may not always draw parts that are 100% complete; for example, you may model only the bounding area and critical features of a purchased part. You still want the mass and volume to be accurately represented in the Properties dialog box.
14 True___ False___ After changing a part’s physical material properties, the part’s color in the graphics window will change to match the material.
15 True___ False___ A derived part can NOT be scaled.
False, a derived part can be scaled and/ or mirrored.
Chapter 09
CHECKING YOUR SKILLS
1. True False - iMates are created while inside of a part file.
TRUE
2 True___ False___ Multiple versions of an iPart can be placed in an assembly.
True
3 True___ False___ When changes are made to an iPart Factory, the changes are automatically updated in iParts that have been placed in assemblies.
False, To update the iParts in an assembly, open the assembly and click the Full Update tool from the Standard toolbar. iParts that need to be updated are marked with an update symbol in the Browser.
4. True False – You can add features to standard iParts after they have been placed in an assembly.
False, Standard iParts can not be modified by adding features to them. The features that comprise Standard iParts are specified upon creation.
5. True False - Named parameters are added automatically as Size parameters during iFeature creation and cannot be removed.
6. What happens when you create a table-driven iFeature and one of the original parameters contains a list of values for the parameter?
A corresponding member is added to the iFeature table for each value that was specified in the List. For example, if a parameter contained a list of three values for a dimension, there would be three individual rows created in the iFeature table.
7. True False – A Design View can control the display style (shaded or wireframe) of an assembly model.
FALSE. While design view representations can control component visibility, color settings, zoom magnification, and viewing angle, they do not control the display style of an assembly model. In other words, if you switch to wireframe, all design view representations are displayed in wireframe mode
8. What is the purpose of a positional representation?
Positional representations are used to show an assembly model in different positional states. They can be used to show a motion study of an assembly model. Each motion segment or kinematical state can represent a different position of the assembly and each state can be saved to a positional representation.
9. When would you want to make an assembly have the Flexible property?
The Flexible property is used when there are multiple instances of a sub-assembly in a main assembly that need to be shown or behave independently of each other.The flexible property allows the same instances to function independently of the other instances.
10. What is the purpose of the Capacity Meter and what information does it display?
The capacity meter displays the number of occurrences in an active assembly file and the number of files in the session. It also displays the amount of free memory that is available to the system as well as the amount of committed or used memory.
11. True False – Creating features in the context of an assembly will update the individual parts that make up the assembly automatically.
FALSE. When an assembly feature is created in the context of an assembly model, the individual parts that make up the assembly will not automatically update to reflect this created feature.
12. True False – A 2D design layout consists of a series of 2D sketches that are constrained to 3D parts in an assembly file.
TRUE
Chapter 10
CHECKING YOUR SKILLS
1 The base feature of a sheet metal part is most often a:
b). Face
2 What is the procedure to change the edges connected by a bend feature?
c). Edit the bend and select the new edges.
3 Which tool would you use to create a full-length rectangular face off an existing face edge?
a). Flange
4 What is required to update a flat pattern model?
d). The flat pattern is updated automatically.
5 True___ False___ Sheet metal parts can contain features created with Autodesk Inventor modeling tools.
6 True___ False___ Sheet Metal Style settings cannot be overridden; a new Style must be created for different settings.
False, you can override specific settings of the current Sheet Metal Style on a per feature basis. Some of the settings that can be overridden are the Unfold Method, Bend Transition, Relief Shape, Relief Width, Relief Depth, Bend Radius, and Minimum Remnant.
7 True___ False___ During the creation of a sheet metal face, it can extend to meet another face and connect to it with a bend.
True
Source: http://www.delmarlearning.com/companions/content/141804914X/instructor/IV11%20Instructors%20Guide%20Rev2.doc
Web site to visit: http://www.delmarlearning.com
Author of the text: indicated on the source document of the above text
If you are the author of the text above and you not agree to share your knowledge for teaching, research, scholarship (for fair use as indicated in the United States copyrigh low) please send us an e-mail and we will remove your text quickly. Fair use is a limitation and exception to the exclusive right granted by copyright law to the author of a creative work. In United States copyright law, fair use is a doctrine that permits limited use of copyrighted material without acquiring permission from the rights holders. Examples of fair use include commentary, search engines, criticism, news reporting, research, teaching, library archiving and scholarship. It provides for the legal, unlicensed citation or incorporation of copyrighted material in another author's work under a four-factor balancing test. (source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fair_use)
The information of medicine and health contained in the site are of a general nature and purpose which is purely informative and for this reason may not replace in any case, the council of a doctor or a qualified entity legally to the profession.
The following texts are the property of their respective authors and we thank them for giving us the opportunity to share for free to students, teachers and users of the Web their texts will used only for illustrative educational and scientific purposes only.
All the information in our site are given for nonprofit educational purposes
The information of medicine and health contained in the site are of a general nature and purpose which is purely informative and for this reason may not replace in any case, the council of a doctor or a qualified entity legally to the profession.
www.riassuntini.com