BIOLOGY EOC REVIEW PACKET
Scientific Method
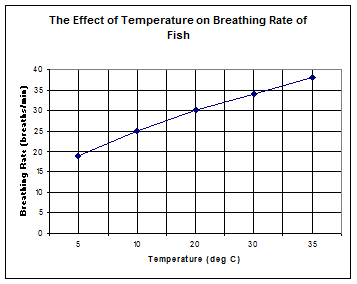
Breathing Rate (breaths/minute) |
Temperature (°C) |
19 |
5 |
25 |
10 |
30 |
20 |
34 |
30 |
38 |
35 |
Temperature, it is the variable that is being changed
Breathing rate, it is the variable that is being measured and it depends on the temperature
Breathing rate increases
Same tank, same fish, same pH of water, same time of day
The breathing rate would increase even more, but if the temperature gets too hot the fish could die.
|
Pumpkin A |
Pumpkin B |
Pumpkin C |
Type of pumpkin seed |
Jack-o-Lantern |
Jack-o-Lantern |
Jack-o-Lantern |
Amount of water given daily (mL) |
29.5 |
29.5 |
29.5 |
Amount of sunlight |
full sunlight |
full sunlight |
full sunlight |
Temperature (oC) |
23.9 |
23.9 |
23.9 |
Amount of fertilizer given (g) |
0 |
200 |
300 |
Type of soil |
organic |
Organic |
Organic |
Day the seeds were planted |
7/8/2007 |
7/8/2007 |
7/8/2007 |
Number of pumpkins that the vine produced. |
3 |
6 |
2 |
How much fertilizer is needed to produce the most pumpkins on the vine.
Amount of fertilizer
Number of pumpkins that the vine produced
Amount of water, amount of sunlight, temperature, type of soil, day the seeds were planted
200g of fertilizer
|
Soda A |
Soda B |
Soda C |
Soda D |
Type of Diet soda |
Diet Coke |
Diet Coke |
Diet Coke |
Diet Coke |
Amount of soda in the container (L) |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
Temperature of surroundings (oC) |
24 |
24 |
24 |
24 |
Temperature of beverage (oC) |
23.9 |
23.9 |
23.9 |
23.9 |
Amount of mentos given (g) |
0 |
3 |
6 |
9 |
Day the mentos were dropped |
7/8/2007 |
7/8/2007 |
7/8/2007 |
7/8/2007 |
Estimated height of the soda geyser (cm). |
0 |
250 |
300 |
300 |
How many Mentos will it take to make the highest Coke geyser.
Amount of Mentos given
Estimated height of soda geyser
Type of soda, amount of soda in bottle, temperature of surrounding, temperature of soda, same day
No, the height for 6g of Menots is the same as 9g of Menots
Chapter 2 – The Chemistry of Life
Organic Molecule: |
Contains which of the following: |
Made up of: |
Function |
Examples |
Carbohydrates |
C, H, O |
Sugars & starches |
|
Glucose |
Lipids |
C, H |
Fatty acid & glycerol |
|
Fats |
Proteins |
C, H, O, N |
Amino Acids |
|
Enzymes |
Nucleic Acids |
C, H, O, N, P |
Nucleotides |
|
DNA |
Acts as a biological catalyst, speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction
Most enzymes work best at body temperature, higher temps will cause the enzyme to no longer work properly
Make up a lot of living things, universal solvent (dissolves many things)
Attraction between water molecules which allows insects and other objects to float a top the water
Chapter 7 – Cell Structure & Function (including Diffusion and Osmosis)
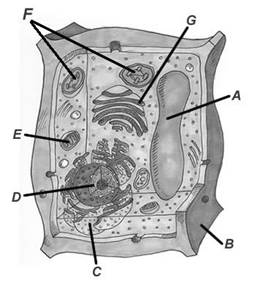
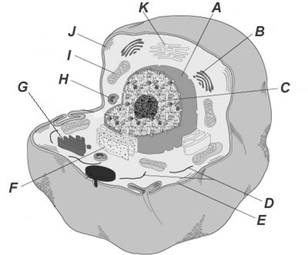
Organelle |
Function |
Nucleus |
Controls the functions of the cell |
Ribosomes |
Make proteins |
Cell membrane |
Regulate what enters and leaves the cell |
Cell wall |
Provides protection and support for plant cells |
Mitochondria |
Creates energy for the cell by breaking down sugar |
Vacuoles |
Stores water, sugar, and other molecules for the cell |
Lysosome |
Cleans up waste in the cell |
Golgi apparatus |
Sorts and packages molecules for transport around the cell |
Chloroplast |
Creates energy for plant cells by converting sunlight into usable energy |
Endoplasmic reticulum |
Make components (parts) for the cell |
Chloroplast
Golgi appartatus
Mitochondria
Lysosome
Cytoskeleton
Cell membrane
Rough ER
Golgi appartatus
Cell membrane
Nucleolus
Golgi appartatus
Smooth ER
Nucleus
Mitochondria
Nucleus
Rough ER
Cell wall
Vacuole
Organelle → Cell → Tissue → Organ → Organ System ***This listing is smallest to largest****
Eukaryotic: have a nucleus, more complex, organelles
Prokaryotic: no nucleus, simple, no membrane-bound organelles
Plant: Cell wall, one large vacuole, chloroplast
Animal: Many small vacuoles, lysosomes, centrioles
Both: Nucleus, ER, golgi apparatus, cell membrane, mitochondria,
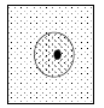
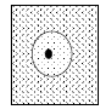
Membrane that allows some things to pass while others cannot
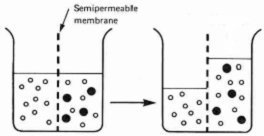 Too large to pass through the membrane
Too large to pass through the membrane
Right
Left
To the left, moves from high to low concentration
![]()
![]()
|
Passive Transport |
Active Transport |
Requires energy? |
NO |
YES |
Low to high or High to low? |
High to Low |
Low to high |
Examples |
Diffusion & osmosis |
Exocytosis & endocytosis |
Chapter 10 – The Cell Cycle & Mitosis
G1: cell growth; G2: cell prepares to divide
The cytoplasm divides
The cell could not control its growth rate and would continue to divide – leads to cancer
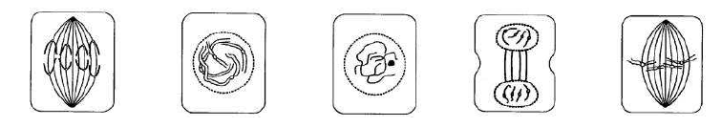
Anaphase Prophase Interphase Telophase Metaphase
|
Mitosis |
Meiosis |
Type of Reproduction (asexual or sexual) |
Asexual |
Sexual |
Chromosome number of parent cell |
2N |
2N |
Chromosome number of daughter cells |
2N |
N |
Number of Cell Divisions |
1 |
2 |
Number of Daughter Cells |
2 |
4 |
When does DNA replication take place? |
Interphase |
Interphase |
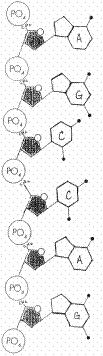 Chapter 12 – DNA & RNA
Chapter 12 – DNA & RNA
T – C – G – G – T – C
Deoxyribose sugar; phosphate groups
Hydrogen bonds
Make RNA from DNA; in the nucleus
U – C – G – G – U – C
Group of 3 bases that codes for an amino acid
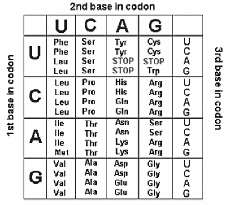 Describe the process of translation and where it happens.
Describe the process of translation and where it happens. Make protein from RNA; in the cytoplasm at the ribosome
Ser – Val
Peptide bond
|
DNA |
RNA |
Sugars |
Deoxyribose |
Ribose |
Bases |
A, T, C, G |
A, U, C, G |
Number of Strands |
2 strands |
1 stand |
Where in the Cell |
Nucleus |
Cytoplasm |
Function |
Stores genetic info |
Transports genetic info |
DNA is copied; DNA unzips, one strand serves as the template and creates 2 new DNA molecules
Two new molecules – made up of one original strand and one new strand
Change in genetic sequence
mRNA – carries message from DNA
rRNA – makes up the ribosome
tRNA – transfers amino acids to the ribosome
Chapter 11 – Intro to Genetics
TT |
Tt |
Tt |
tt |
Tt x Tt
75% Tall
25% short
Tt |
tt |
Tt |
tt |
tt x Tt
50% short
50% Tall
Tt x tt
Key: RR = red WW = white RW = pink
RW x RW
RR |
RW |
RW |
WW |
25% red
50% pink
25% white
IA IA |
IA IA |
IA IB |
IA IB |
Mr. Jones: IAIA
Mrs. Jones: IAIB
50% chance of a child with Type A blood
Yes only if Mom is IAi and Dad is IBi.
Most sex-linked traits are on the X chromosome, males only need one affected gene to get the trait
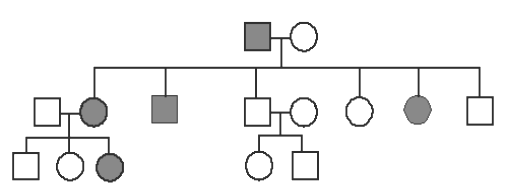
I 1 2
II 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
III 1 2 3 4 5
bb
Bb
bb x bb
100% chance of being affected
Chapter 1 – The Science of Biology
The ability of an organism to maintain its internal environment despite conditions in the external environment
Chapter 8 & 9 – Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
CO2 + H2O + Energy → C6H12O6 + O2
Carbon dioxide + water + sunlight → glucose + oxygen
Reactants: carbon dioxide, water
Products: glucose, oxygen
C6H12O6 + O2 → CO2 + H2O + Energy
glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + energy + water
Reactants: glucose, oxygen, water
Products: energy, carbon dioxide, water
Light intensity, Color of light, amount of water, temperature, amount of carbon dioxide
Chapter 15 - Evolution
“Survival of the Fittest” - MOST fit will survive and reproduce and the least fit die or have few offspring
Two organisms directly affect each other’s evolution
EX: honeybee and flower, hummingbirds and flowers
All living things compete for resources, only those that are best adapted will obtain those resources. Those that are BEST FIT will survive, reproduce, and pass on those traits to their offspring. Those that are least fit will die.
Chapter 18 - Classification
Two – plants and animals
Then realized that it wasn’t enough to categorize every organism.
Kingdom
Phylum
Class
Order
Family
Genus
Species
Two word naming system – Genus species
Organism B: Coleoptera
Organism A: Arachnida
A
C
B



Dichotomous Key:
1. a. The animal has eight legs …Arachnida
b. The animal has six legs … go to 2
2. a. The animal has spots … Coleoptera
b. The animal has stripes … Lepisiota
Organism C: Lepisiota
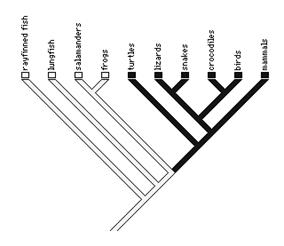
Ray-finned fish
They are the closest on the cladogram, so they are the most similar
Nonliving, they contain DNA, but cannot reproduce. They most use a host to reproduce.
Bacteria: ALIVE, prokaryotes, unicellular
Viruses: NOT LIVING, DNA enclosed in a capsid, much smaller than a bacteria
Chapter 3 & 4 – Ecosystems
Feet, lungs, protective skin – prevent water loss, fur
Roots, cuticle to prevent water loss, stems
Biotic – living factors (food, predators, competitors)
Abiotic – non living factors (sunlight, temperature, water, pH)
The maximum amount of individuals in a population that the surrounding environment can sustain
Plants use photosynthesis to make their own food, other organisms then rely on plants for their food, other animals rely on those herbivores
They break down matter so it can be recycled back into the environment
Each level in a food chain or food web (producers, primary consumers, secondary consumers)
A series of steps in which organisms transfer energy by eating and being eaten
Links all food chains together in an ecosystem
SUN
Oak tree – blossoms, nuts, leaves
Bees, deer, mice, rabbit, insects
Wolf, Bear, toad, birds, red fox, skunk
Bear, wolf, red fox
BEAR
Create an energy pyramid from the food chain: leaves → insects → birds → red fox → bear
RED FOX
BIRDS
Where is the most energy in this pyramid? Where is the least energy?INSECTS
LEAVES
What happens to energy as it moves through the food chain/web?Only 10% of energy is available from the before
Bear – 1 kilocalorie
Red fox – 10 kilocalories
Birds – 100 kilocalories
Insects – 1,000 kilocalories
Leaves – 10,000 kilocalories
Matter is recycled – carbon cycle, water cycle,
Source: http://www.glasgow.k12.ky.us/userfiles/48/Classes/381//userfiles/48/my%20files/eoc%20review%20packet%20answers.doc?id=28425
Web site to visit: http://www.glasgow.k12.ky.us
Author of the text: not indicated on the source document of the above text
If you are the author of the text above and you not agree to share your knowledge for teaching, research, scholarship (for fair use as indicated in the United States copyrigh low) please send us an e-mail and we will remove your text quickly. Fair use is a limitation and exception to the exclusive right granted by copyright law to the author of a creative work. In United States copyright law, fair use is a doctrine that permits limited use of copyrighted material without acquiring permission from the rights holders. Examples of fair use include commentary, search engines, criticism, news reporting, research, teaching, library archiving and scholarship. It provides for the legal, unlicensed citation or incorporation of copyrighted material in another author's work under a four-factor balancing test. (source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fair_use)
The information of medicine and health contained in the site are of a general nature and purpose which is purely informative and for this reason may not replace in any case, the council of a doctor or a qualified entity legally to the profession.
The following texts are the property of their respective authors and we thank them for giving us the opportunity to share for free to students, teachers and users of the Web their texts will used only for illustrative educational and scientific purposes only.
All the information in our site are given for nonprofit educational purposes
The information of medicine and health contained in the site are of a general nature and purpose which is purely informative and for this reason may not replace in any case, the council of a doctor or a qualified entity legally to the profession.
www.riassuntini.com