What is technical documentation?
What is a manual?
Why do we need manuals?
Which information do we find there?
Technical documentation
= refers to any type of documentation that describes handling, functionality, construction and use of a technical product.
Documentation may include:
Assembly manual
= means instructions
Manual consist of:
User guide includes:
What is technical drawing?
Which information does a technical drawing include?
What can you see in the drawing?
Which information can you read from the drawing?
Technical drawing
= clearly defines requirements for appliances, includes the drawing of picture and graphical language that communicates ideas and information It communicates all needed information from the engineer to the workers who will make it.
It includes following information:
THE ENGINE
There are four engine cycles: INTAKE, COMPRESSION, POWER, EXHAUST
INTAKE stroke: on the intake or induction stroke of the piston, the piston descends from the top of the cylinder to the bottom of the cylinder, reducing the pressure inside the cylinder. A mixture of fuel and air, or just air in a diesel engine, is forced by atmospheric (or greater) pressure into the cylinder through the intake port. The intake valve(s) then close. The volume of air/fuel mixture that is drawn into the cylinder, relative to the volume of the cylinder is called, the volumetric efficiency of the engine.
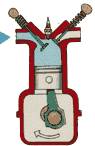
COMPRESSION stroke: with both intake and exhaust valves closed, the piston returns to the top of the cylinder compressing the air, or fuel-air mixture into the combustion chamber of the cylinder head.
POWER stroke: this is the start of the second revolution of the engine. While the piston is close to Top Dead Centre, the compressed air–fuel mixture in a gasoline engine is ignited, usually by a spark plug, or fuel is injected into the diesel engine, which ignites due to the heat generated in the air during the compression stroke. The resulting massive pressure from the combustion of the compressed fuel-air mixture forces the piston back down toward bottom dead centre.
EXHAUST stroke: during the exhaust stroke, the piston once again returns to top dead centre while the exhaust valve is open. This action evacuates the burnt products of combustion from the cylinder by expelling the spent fuel-air mixture out through the exhaust valve(s).
1st phase - INTAKE: The mixture of air and fuel is drawn into the cylinder.
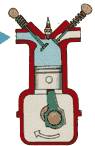
2nd phase - COMPRESSION stroke: The mixture is compressed – the pressure and temperature are increasing.

3rd phase - POWER stroke: The mixture is ignited. The piston is pushed down by the burnt products.

4th phase - EXHAUST stroke: This action evacuates the burnt products of combustion from the cylinder.





Link the engine parts with the materials and processes.
cylinders cast iron
piston hard steel
oil sump hard aluminium
oil filter cover forged steel
camshaft plastic
cylinder head light aluminium alloy
compression rings normal aluminium
connection rods aluminium alloy with a graphite coating
engine block cast iron
Source: http://www.sosasou-vocelova.cz/wp-content/uploads/2015/12/Technical-documentation.doc
Web site to visit: ttp://www.sosasou-vocelova.cz
Author of the text: indicated on the source document of the above text
If you are the author of the text above and you not agree to share your knowledge for teaching, research, scholarship (for fair use as indicated in the United States copyrigh low) please send us an e-mail and we will remove your text quickly. Fair use is a limitation and exception to the exclusive right granted by copyright law to the author of a creative work. In United States copyright law, fair use is a doctrine that permits limited use of copyrighted material without acquiring permission from the rights holders. Examples of fair use include commentary, search engines, criticism, news reporting, research, teaching, library archiving and scholarship. It provides for the legal, unlicensed citation or incorporation of copyrighted material in another author's work under a four-factor balancing test. (source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fair_use)
The information of medicine and health contained in the site are of a general nature and purpose which is purely informative and for this reason may not replace in any case, the council of a doctor or a qualified entity legally to the profession.
The following texts are the property of their respective authors and we thank them for giving us the opportunity to share for free to students, teachers and users of the Web their texts will used only for illustrative educational and scientific purposes only.
All the information in our site are given for nonprofit educational purposes
The information of medicine and health contained in the site are of a general nature and purpose which is purely informative and for this reason may not replace in any case, the council of a doctor or a qualified entity legally to the profession.
www.riassuntini.com